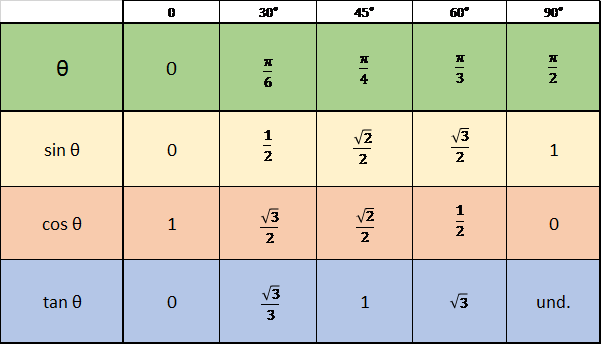
Sin And Cos Chart . It leads to this very handy chart. Sin 60° = √3/4 = √3/2.
Understanding The Unit Circle | Studypug from www.studypug.com
Cos 30° = √(3/4) = √3/2 This is something that most mathematicians keep on chanting and we believe you also must have come across the same. During calculations involving sine, cosine, or tangent ratios, we can directly refer to the trig chart given in the following section to make the deductions easier.
Understanding The Unit Circle | Studypug
During calculations involving sine, cosine, or tangent ratios, we can directly refer to the trig chart given in the following section to make the deductions easier. Cos 0° = √(4/4) = 1. Cos 30° = √(3/4) = √3/2 Sin(2a) = 2cosasina sin(2a) =2cosasina.
Source: cochranmath.pbworks.com
Thus, we can get the values of tan ratio for the specific angles. Trignometry table of sin cos tan cosec sec cot is useful to learn the common angles of trigonometrical ratios are 0 30 45 60 90 180 270 and 360. Cos 30° = √(3/4) = √3/2 Sine and cosine — a.k.a., sin(θ) and cos(θ) — are functions revealing.
Source: www.pinterest.com
Sin0 30 45 60 90 cos90 60 45 30 0 sqrt0 1 2 3 44 basic trigonometric identities. Looking out from a vertex with angle θ, sin(θ) is the ratio of the opposite side to the hypotenuse, while cos(θ) is the ratio of the adjacent side to the hypotenuse. Sine cosine other and in general terms of powers of sin.
Source: fakeintensive.weebly.com
Sin 45° = √(2/4) = 1/√2. Sine and cosine — a.k.a., sin(θ) and cos(θ) — are functions revealing the shape of a right triangle. This is something that most mathematicians keep on chanting and we believe you also must have come across the same. Apart from these identities, we have a few more formulas which are helpful for you in.
Source: math.stackexchange.com
Sin0 30 45 60 90 cos90 60 45 30 0 sqrt0 1 2 3 44 basic trigonometric identities. 3 2;cos2 ax (65) z sin3 axdx= 3cosax 4a + cos3ax 12a (66) z cosaxdx= 1 a sinax (67) z cos2 axdx= x 2 + sin2ax 4a (68) z cosp axdx= 1 a(1 + p) cos1+p ax 2f 1 1 + p.
Source: exceltable.com
Sin 2𝜃=2 sin𝜃 cos𝜃 cos 2 𝜃 = cos 2𝜃−sin2𝜃 =2 cos2θ−1 =1−2 sin2𝜃 tan 2𝜃= 2 tan𝜃 1−tan2𝜃 Find here the tangent values table from 0 to 360 degrees. 47 rows for sin, we know. Cos 0° = √(4/4) = 1. They’re the next step on the road to mastery of the unit circle.
Source: www.wikihow.com
Sin(2a) = 2tana 1 + tan2a sin(2a) = 2tana 1+tan2a. 3 + p 2;cos2 ax (69) z cos3 axdx= 3sinax 4a + sin3ax 12a (70) z cosaxsinbxdx= cos[(a b)x] 2(a b) cos[(a+ b)x] 2(a+ b);a6= b (71) z sin2 axcosbxdx=. Thus, we can get the values of tan ratio for the specific angles. Sin2 axdx= x 2 sin2ax 4a (64).
Source: improveyourmathfluency.com
Sin(35°) = opposite / hypotenuse = 2.8/4.9 = 0.57. Looking out from a vertex with angle θ, sin(θ) is the ratio of the opposite side to the hypotenuse, while cos(θ) is the ratio of the adjacent side to the hypotenuse. In mathematics, sine and cosine are trigonometric functions of an angle. Sin 60° = √3/4 = √3/2. 3 + p.
Source: www.mathsisfun.com
Sin hypotenuse q= hypotenuse csc opposite q= adjacent cos hypotenuse q= hypotenuse sec adjacent q= opposite tan adjacent q= adjacent cot opposite q= unit circle definition for this definition q is any angle. Sin(2a) = 2tana 1 + tan2a sin(2a) = 2tana 1+tan2a. Cartesian coordinates using cartesian coordinates we mark a point on a graph by how far along and.
Source: www.cliffsnotes.com
Sin cos tan chart/table is a chart with the trigonometric values of sine, cosine, and tangent functions for some standard angles 0 o, 30 o, 45 o, 60 o, and 90 o. Trignometry table of sin cos tan cosec sec cot is useful to learn the common angles of trigonometrical ratios are 0 30 45 60 90 180 270 and.
Source: www.cuemath.com
Sin 45° = √(2/4) = 1/√2. Cos 0° = √(4/4) = 1. Tan(2a) = 2tana 1 − tan2a tan(2a) = 2tana 1 −tan2a. 47 rows for sin, we know. Since 120 lies in ii quadrant cos is negative.
Source: www.math-only-math.com
Sin cos tan chart/table is a chart with the trigonometric values of sine, cosine, and tangent functions for some standard angles 0 o, 30 o, 45 o, 60 o, and 90 o. Since 120 lies in ii quadrant cos is negative. Sin(2a) = 2tana 1 + tan2a sin(2a) = 2tana 1+tan2a. No matter the size of the triangle, the values.
Source: www.sampletemplates.com
Sin2 axdx= x 2 sin2ax 4a (64) z sinn axdx= 1 a cosax 2f 1 1 2; A circle centered at the origin of the coordinate system and with a radius of 1 is known as a unit circle. 3 2;cos2 ax (65) z sin3 axdx= 3cosax 4a + cos3ax 12a (66) z cosaxdx= 1 a sinax (67) z cos2.
Source: www.studypug.com
S ilver sin and cosec function are positive rest are negative in ii quadrant. The sine and cosine of an acute angle are defined in the context of a right triangle: Trignometry table of sin cos tan cosec sec cot is useful to learn the common angles of trigonometrical ratios are 0 30 45 60 90 180 270 and 360..
Source: in.pinterest.com
Sin hypotenuse q= hypotenuse csc opposite q= adjacent cos hypotenuse q= hypotenuse sec adjacent q= opposite tan adjacent q= adjacent cot opposite q= unit circle definition for this definition q is any angle. It leads to this very handy chart. So, for cosec it will be. Sin 90° = √(4/4) = 1. Sin cos tan chart/table is a chart with.
Source: www.ambrsoft.com
Sin0 30 45 60 90 cos90 60 45 30 0 sqrt0 1 2 3 44 basic trigonometric identities. Sin(35°) = opposite / hypotenuse = 2.8/4.9 = 0.57. Sine, cosine, and tangent table: Sin hypotenuse q= hypotenuse csc opposite q= adjacent cos hypotenuse q= hypotenuse sec adjacent q= opposite tan adjacent q= adjacent cot opposite q= unit circle definition for this.
Source: improveyourmathfluency.com
The positive and negative values for each quadrant. The values that include pi, π, are called radians. The sine and cosine of an acute angle are defined in the context of a right triangle: They’re the next step on the road to mastery of the unit circle. Trignometry table of sin cos tan cosec sec cot is useful to learn.
Source: www.shutterstock.com
As we know, tan is the ratio of sin and cos, such as tan θ = sin θ/cos θ. If p is a point from the circle and a is the angle between po and x axis then: Sin 45° = √(2/4) = 1/√2. The sine and cosine of an acute angle are defined in the context of a right.
Source: quizlet.com
So, for cosec it will be. And put them all together. So for cosec it will be. Sine, cosine, and tangent table: Sin2 axdx= x 2 sin2ax 4a (64) z sinn axdx= 1 a cosax 2f 1 1 2;
Source: www.tes.com
47 rows for sin, we know. Thus, we can get the values of tan ratio for the specific angles. For the specified angle, its sine is the ratio of the length of the side that is opposite that angle to the length of the longest side of the triangle (the hypotenuse), and the cosine is the ratio of the length.
Source: www.mathsisfun.com
No matter the size of the triangle, the values of sin(θ) and cos(θ) are the same for a given θ, as illustrated below. So for cosec it will be. Sin hypotenuse q= hypotenuse csc opposite q= adjacent cos hypotenuse q= hypotenuse sec adjacent q= opposite tan adjacent q= adjacent cot opposite q= unit circle definition for this definition q is.